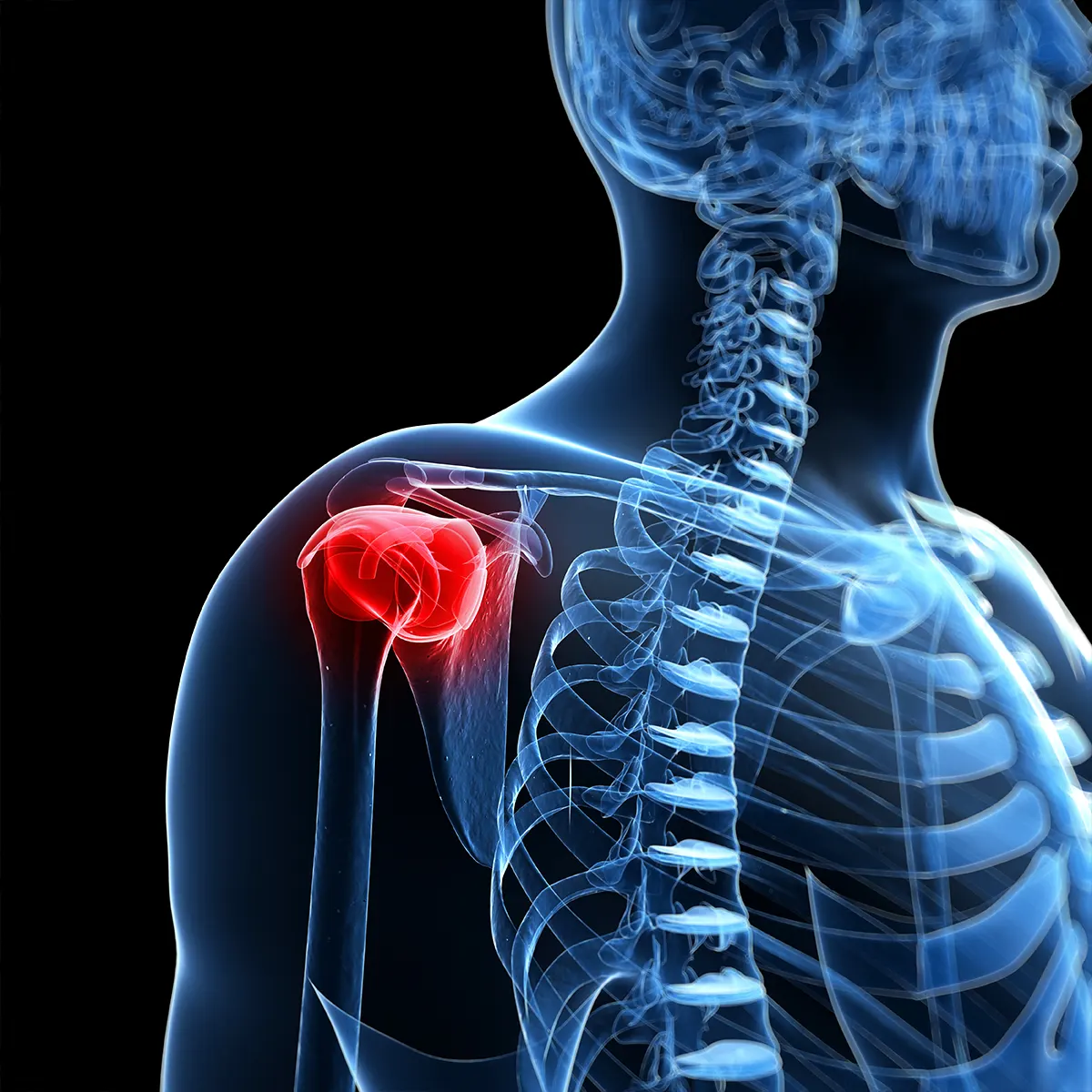
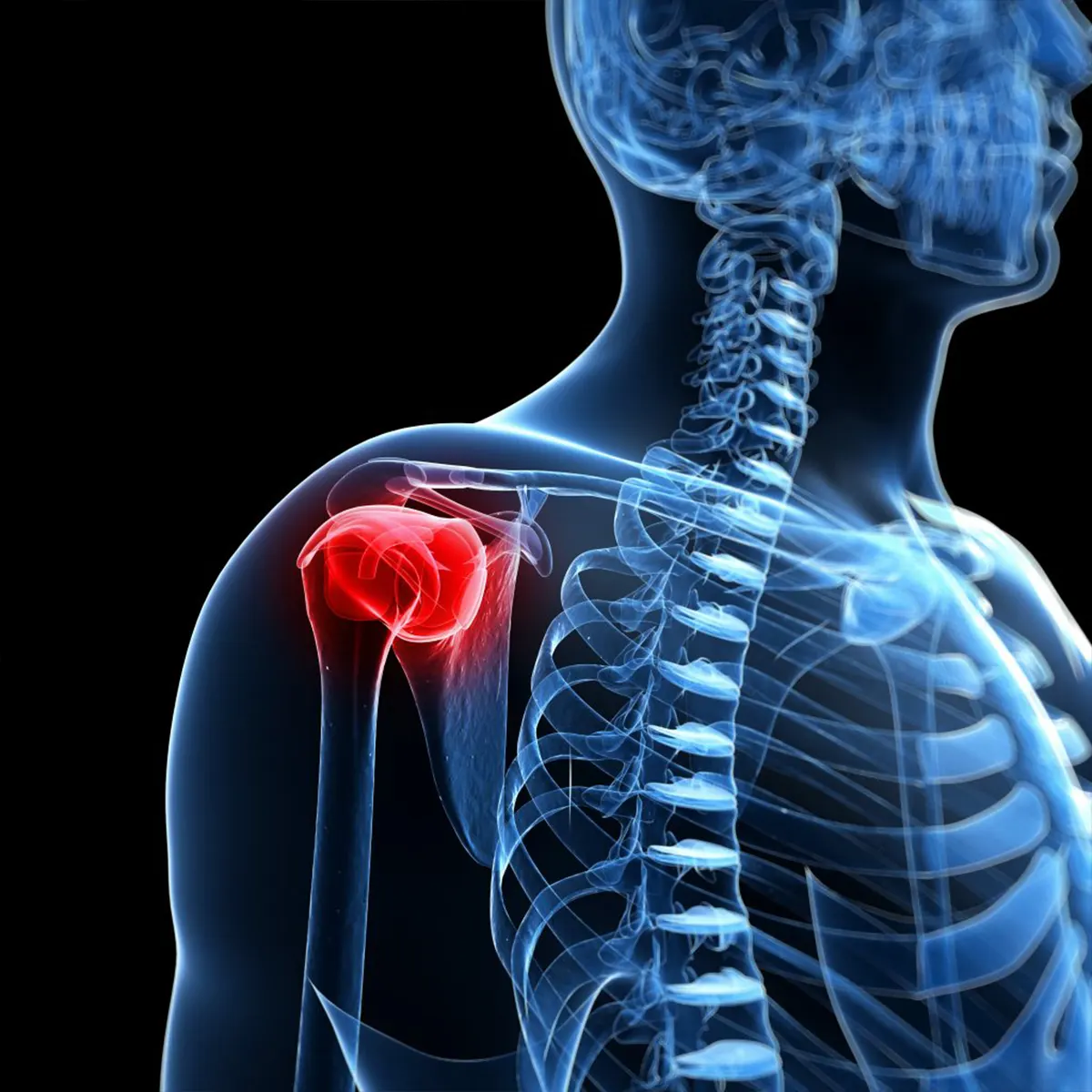
Rotator Cuff Injuries are quite common in Kenya. Rotator Cuff Tear can be caused by wear and tear of the tendon over time or repetitive impactful actions such as those in sports. Rotator cuff tears occur when tendons pull away from your arm bone. A tear may result from overuse or another injury, which may even cause the inability to use your arm. Rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons in your shoulder. They help you lift and move your arms away from your body. Your rotator cuff keeps the ball of your upper arm bone (humerus) in the shoulder blade socket.
A partial or complete rotator cuff tear makes it difficult to raise and move your arm, which may cause shoulder pain and arm weakness. Rotator cuff injuries are common in Kenya and more common in older patients. Rest, pain relievers and physiotherapy may help. Some patients may need surgery to reattach a torn rotator cuff.
Rotator Cuff Tear Types
Rotator cuff injury has two types of tears:
- Partial Rotator Cuff Tear - With a partial tear, your tendon still somewhat is attached to your arm bone.
- Complete Rotator Cuff Tear - With a full thickness or a complete tear, your tendon is separated completely from your bone. There is a hole or rip in your tendon.
Rotator Cuff Tear Causes
Commonly, rotator cuff tear occurs over time as your tendon wears down with use and age, also called a degenerative tear. People over age 40 are at most risk. An accident, such as a fall, can cause a broken collarbone or dislocated shoulder, which can cause a rotator cuff injury.
Causes of degenerative rotator cuff tears include:
- Bone Spurs are bony growths can form on top of the shoulder bone. These bone spurs rub against your tendon when you lift your arm. This shoulder impingement creates friction between your bone and tendon. Overtime, a partial or complete tear may occur.
- Decreased Blood Flow to your rotator cuff occurs as you get older. Your muscles and tendons need a healthy blood supply to repair themselves. Lack of thereof to your tendons, can cause a rotator cuff tear.
- Overuse, such as repetitive shoulder movements during sports or on the job can stress your muscles and tendons, causing a tear.
rotator cuff injury symptoms
Rotator cuff injury symptoms usually include:
- Difficulty, pain and weakness caused by raising, lowering or rotating your arm.
- Popping, clicking or crackling sounds or sensations when moving your arm in certain positions.
- Shoulder pain that worsens at night or when resting your arm.
- Shoulder weakness and struggling to lift items.
rotator cuff injury Diagnosis
Orthopaedic surgeon will perform a physical exam to check for shoulder tenderness, arm strength and range of motion.
To assist with a diagnosis, you may need to get:
- X-ray to check for arthritis or bone spurs.
- MRI or ultrasound to search for tendon tears.
rotator cuff injury treatment
Rotator cuff tear treatment may include nonsurgical and surgical options, such as shoulder arthroscopy.
Rotator cuff tear does not heal on its own without surgery, however, you can improve functionally and decrease pain with nonsurgical treatments by strengthening your shoulder muscles. Having a rotator cuff tear doesn’t necessarily mean you need a surgery, in fact, many people have rotator cuff tears and don’t even know it. About 8 out of 10 people with partial tears can get better with nonsurgical treatments. It can take up to around a year for the condition to improve.
Nonsurgical treatments include:
- Arm sling and rest to give your shoulder time to heal. You may need to modify physical activities and stop some work or sports for a period of time.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to help with pain and swelling.
- Physiotherapy.
- Steroid injections to ease pain and swelling.
For a partial rotator cuff tear, orthopaedic doctor may only need to trim fraying pieces of a partially torn tendon. This debridement procedure keeps your shoulder ball and socket from catching on your tendon and tearing it further.
Unfortunatelly, some rotator cuff tears can’t be repaired due to their size and/or the age of the tear. For such types of tears, you may need reverse shoulder replacement, tendon transfer or a debridement of scar tissue without repair.
rotator cuff surgery
Ready to book an appointment?
Other Shoulder Conditions