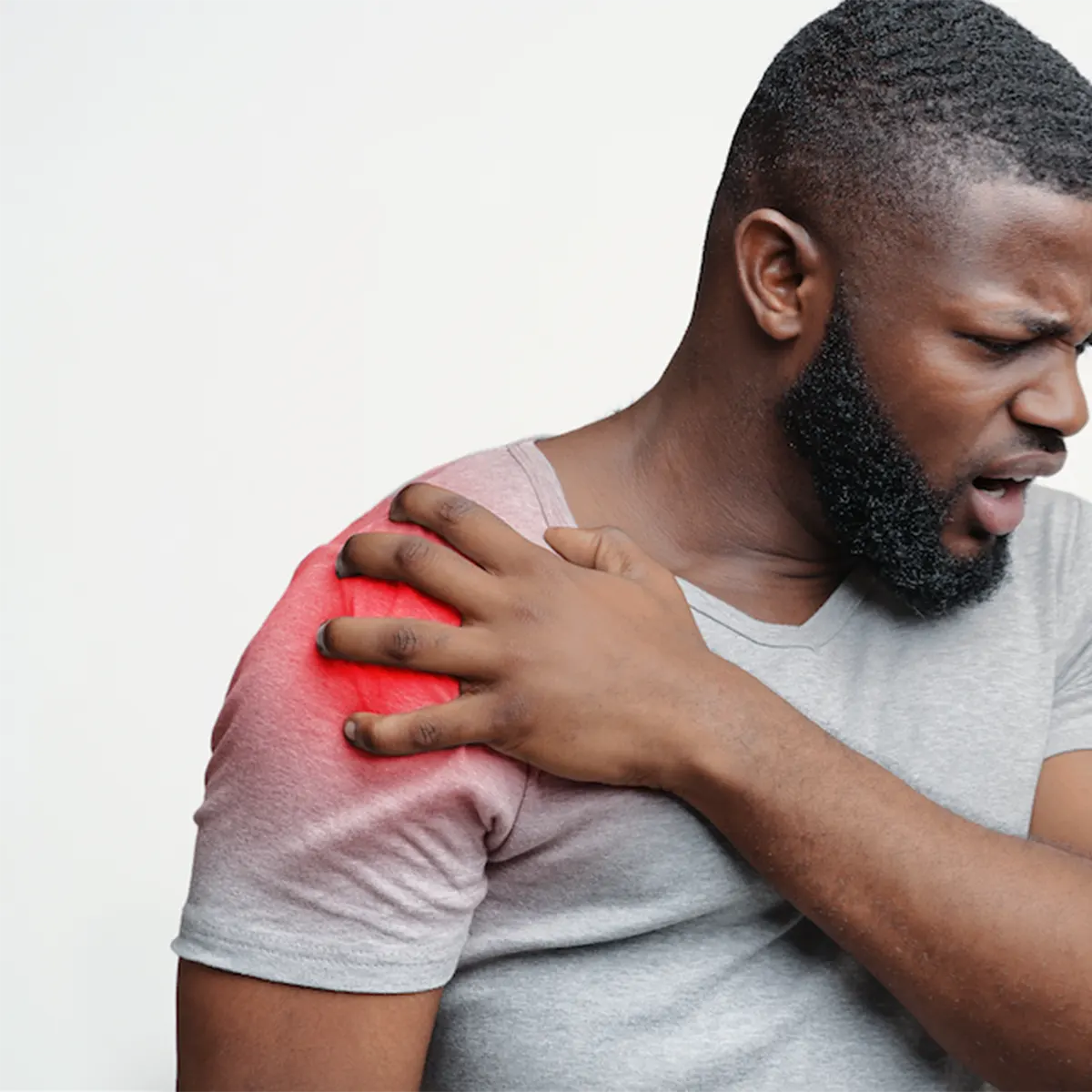
Sprains and strains are common injuries that affect the body’s connective tissues. A sprain occurs when ligaments, the bands of tissue that link two bones, are damaged due to twisting or wrenching a joint. Conversely, a strain involves injuries to muscles or tendons—tendons are the fibrous tissues that attach muscles to bones—often resulting from overuse or excessive force. The ankle is particularly prone to these types of injuries, making it one of the most frequently affected joints.
Causes of Sprains and Strains
A sprain happens when you overstretch or tear a ligament while putting stress on a joint. Sprains commonly occur in the following situations:
- Ankle Joint: Walking or exercising on an uneven surface, or landing awkwardly after a jump.
- Knee Joint: Pivoting during sports activities.
- Wrist: Landing on an outstretched hand during a fall.
- Thumb: Overextension while playing racquet sports, such as tennis.
Sprains and Strains Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of a sprain can vary depending on the severity of the injury and may include:
- Pain in the affected area.
- Swelling of the joint.
- Bruising in the affected area.
- Difficulty moving the affected joint.
- Hearing or feeling a pop in your joint at the time of injury.
prevention of Sprains and Strains
Regular, consistent stretching and strengthening exercises, as part of an overall physical conditioning program, can help minimize the risk of sprains. It’s important to be in shape to play your sport, rather than using your sport to get in shape. For those with physically demanding jobs, regular conditioning can also help prevent injuries.
You can protect your weaker joints in the long term by strengthening and conditioning the muscles around them. Consult your sports medicine doctor for appropriate conditioning and stability exercises. Additionally, use footwear that offers support and protection.
how to treat Sprains and Strains
Prompt first-aid care can help reduce pain and swelling immediately after a knee injury. You should follow the R.I.C.E. method of self-care at home:
- Rest: Immediate rest is necessary for healing and limits weight bearing on your knee.
- Ice: When you're awake, ice your knee every two hours for 20 minutes at a time.
- Compression: Wrap an elastic bandage or compression wrap around the injured knee.
- Elevation: Lie down with your injured knee propped up on a cushion or pillow.
When to see Sports Medicine Doctor
Mild sprains can be treated at home. However, the injuries that cause sprains can also lead to serious conditions, such as fractures. You should see a sports doctor in Nairobi if you:
- Have trouble moving or bearing weight on the affected joint.
- Experience pain directly over the bones of an injured joint.
- Experience numbness in any part of the injured area.
Ready to book an appointment?
Explore more specialties